What Is Pain In The Heel And Ideas On How To Treat It
Overview
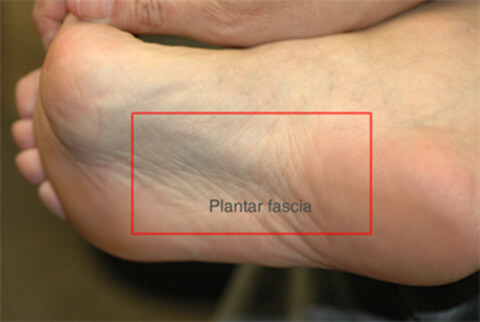
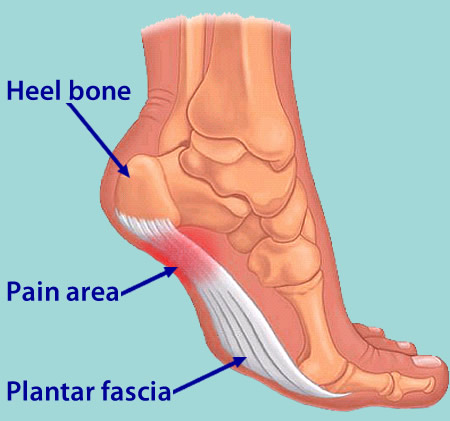
The American College of Sports and Medicine (1) estimates that the average adult takes between 5,000 and 10,000 steps per day. The brunt of this activity is borne by the bones, muscles and ligaments of the foot. Healthy feet have strong, wonderfully flexible ligaments which are designed to support standing, walking and running. Plantar Fasciitis (pronounced "plantar fash-ee-eye-tis") is defined as inflammation of, or damage to, one of the most important ligaments in the foot - the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia ligament is located along the sole of your foot. It is made up of fibrous tissue that stretches outward from the heel bone, like a strong piece of elastic, and then branches out across the arch and through the ball area of the foot toward the toes.
Causes
As a person gets older, the plantar fascia becomes less like a rubber band and more like a rope that doesn't stretch very well. The fat pad on the heel becomes thinner and can't absorb as much of the shock caused by walking. The extra shock damages the plantar fascia and may cause it to swell, tear or bruise. You may notice a bruise or swelling on your heel. Other risk factors for plantar fasciitis include being overweight and obesity. Diabetes. Spending most of the day on your feet. Becoming very active in a short period of time. Being flat-footed or having a high arch.
Symptoms
If you have Plantar Fasciitis, you will most likely feel a sharp pain under the ball of you heel and it will often give pain when standing after a period of rest. For example when you get out of bed in the mornings or after being sat down. Some patients describe this feeling as a stone bruise sensation, or a pebble in the shoe and at times the pain can be excruciating. Patients with Plantar Fasciitis can experience pain free periods whereby the think they are on the mend, only for the heel pain to come back aggressively when they appear to have done nothing wrong. If your plantar fasciitis came on very suddenly and the pain is relentless, then you may have Plantar Fascial Tears. We will be able to differentiate between these 2 conditions, sometimes with ultra sound imaging. The treatment for each of these conditions will need to be very different.
Diagnosis
A physical exam performed in the office along with the diagnostic studies as an x-ray. An MRI may also be required to rule out a stress fracture, or a tear of the plantar fascia. These are conditions that do not normally respond to common plantar fasciitis treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
No single treatment works best for everyone with plantar fasciitis. But there are many things you can try to help your foot get better. Give your feet a rest. Cut back on activities that make your foot hurt. Try not to walk or run on hard surfaces. To reduce pain and swelling, try putting ice on your heel. Or take an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) or naproxen (such as Aleve). Do toe stretches , calf stretches and towel stretches several times a day, especially when you first get up in the morning. (For towel stretches, you pull on both ends of a rolled towel that you place under the ball of your foot.) Get a new pair of shoes. Pick shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole. Or try heel cups or shoe inserts ( orthotics ). Use them in both shoes, even if only one foot hurts. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may recommend splints that you wear at night, shots of medicine (such as a steroid ) in your heel, or other treatments. You probably will not need surgery. Doctors only suggest it for people who still have pain after trying other treatments for 6 to 12 months.
Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with plantar fasciitis are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don't improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. While the success rate is very high following surgery, one should be aware that there is often a prolonged postoperative period of discomfort similar to the discomfort experienced prior to surgery. This pain usually will abate within 2-3 months. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.